
Pair of Blue-and-Yellow Macaws (Ara ararauna) / Photo: Hyacinth Macaw Institute.
You already know the hyacinth macaw and the red-and-green macaw, but we are still missing another species that we study here at the Hyacinth Macaw Institute, the famous and most common sighting, the blue-and-yellow macaw (Ara ararauna).
Here on our site, we have already told you what we do at the Urban Birds Project, that counts on monitoring and research of the blue-and-yellow macaw in the city of Campo Grande – MS for its conservation. But do you really know this species? Continue to the end and we will tell you more about it.
Species characteristics
The Blue-and-Yellow Macaws also belong to the psittacidae family and have common characteristics among the other species of macaws.
Their main morphological characteristics are their smaller size, which can reach a maximum of 86 cm and weigh between 995 to 1380g, their unmistakable coloring, being blue on their back, yellow on their belly, having a white face with black facial feathers near their neck and the front of their head that is green.

Details of its feathers on the face / Photo: Flávia Zagury – Hyacinth Macaw Institute.
Like the other macaws, the vocalization of this species is loud and strong, but each one produces different sounds, and it is possible to distinguish the species by their singing.
Distribution
The blue-and-yellow macaw has a wide distribution throughout South America, being found in Colombia, the Guyanas, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Paraguay, Argentina, and of course in Brazil, and also in Central American countries such as Panama.
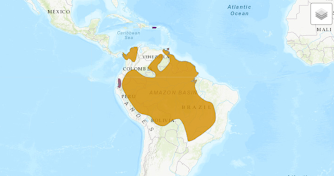
Distribution of the Blue-and-Yellow Macaw (Ara ararauna) / Photo: IUCN.
In Brazil, this bird inhabits many biomes: from the Atlantic Forest to the Amazon and from the Pantanal to the Cerrado.
However, with the excessive amount of deforestation and degradation of its habitats by humans, this macaw has adapted to some cities, such as Campo Grande in Mato Grosso do Sul, which became known as the “capital of macaws.”.

Blue-and-yellow macaws in the city of Campo Grande – MS / Photo: Larissa Tinoco – Hyacinth Macaw Institute.
They were able to adapt to the urban environment because of the fruit trees present in the city, on which they feed, and because they have suitable places for reproduction.
Because of the increase in the number of individuals there, a law was created to make the hyacinth macaw the symbol of the city. With this, the responsible bodies have/span> increased the campaigns to spread the word about the importance of the species and the local biodiversity. This practice also contributes to the increase in tourism in the city, helping the local economy. .
Feeding
These birds have a very varied diet. They can eat mainly fruits and seeds, helping in their dispersal, but they also eat shoots, flowers, and nectar, as well as preying on some plant species.

Blue-and-yellow macaw Feeding / Photo: Larissa Tinoco – Hyacinth Macaw Institute.
Its feeding is wide-ranging, due to the fact that this bird checks the availability and ease of capturing food and also the energy return that this food will provide, but varies according to the location.
Reproduction
To ensure reproductive success, the availability of nests is a determining factor. They depend on the trunks of dead palm trees, using small openings they find to build their nests.
The macaws enlarge these openings to make the space more suitable and use that same nest for years.

Pair of Blue-and-Yellow Macaws / Photo: Larissa Tinoco – Hyacinth Macaw Institute.
Since many individuals inhabit urban areas, it isextremely important that the city be well wooded, in order to maintain healthy populations, reproducing adequately.
In addition, environmental factors (such as rainfall, temperature, and available food, among others) influence the breeding season, egg laying, and even egg incubation.
However, it has been observed that in the cities, other factors even so, the Blue-and-Yellow Macaw has shown itself to be resilient, and has been successful, as it continues to breed in the city of Campo Grande, where our research with the species takes place.
We continue to monitor these birds,to analyze whether other impacts and consequences could affect them in the future.

Chick of the Blue-and-Yellow Macaw monitored in Campo Grande – MS / Photo: Flávia Zagury – Hyacinth Macaw Institute.
The reproductive period of the Ara ararauna This period is designated from the moment there is an active nest until the moment the last juvenile individual leaves the nest and flies away.
Copulation basically takes place between July and August, and the number of eggs laid varies from 2 to 4, also occurring in August. The chicks are born in September, and the juveniles begin to leave the nest in December.
Of course, these periods can change due to different external factors. However, while they occur, the parents are doing nest defense and parental care of the chicks.
Threats
Mainly because this species is quite used to the cities, urban impacts become frequent, such as noise pollution, electrocution by electric cables, attacks by domestic animals, collisions with buildings, accidents with kite strings, being run over by cars, and conflicts with human beings.
Human action is also a determining factor in the health of the species, such as the destruction, pollution, and deforestation of their natural habitat, as well as hunting to traffic them as domestic animals, a factor that affects more than 38 million animals a year, completely threatening biodiversity.
Unfortunately, the Blue-and-Yellow Macaw is one of the psittaciformes more captured by traffickers in the wild here in the country, due to its plumage, its adaptation to other environments, and its ability to imitate words.
Its conservation status globally,, fortunately, is classified as Least Concern by the IUCN, but its populations continue to decline due to the factors mentioned above.
Therefore, it is extremely important that the population continues to be informed and that environmental education activities are developed so that we can improve our relationship with fauna.
Text by: Giovanna Leite Batistão
Reviewed by: Juliana Cuoco Badari
